
|

|

|

|
|
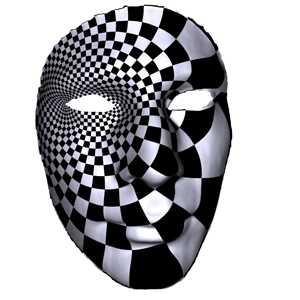
face.m
|
face_0.open.m
|
face_1.open.m
|
face.open.m
|

|

|

|

|
|
face_1.du.m
|
face_2.du.m
|
face_0.dv.m
|
face_1.dv.m
|
|

|

|

|
|
face_0.duv.m
|
face_1.duv.m
|
face_2.duv.m
|
face_3.duv.m
|
Algorithm Description
Computing holomorphic 1-form basis for poly annulus mesh. Computing a special holomorphic 1-form, such that the mesh is mapped to a stripe,
two boundaries are mapped to the upper and lower sides of the stripe, other boundaries are mapped to horizontal slits.
Input and output
The input is a poly annulus
- A genus zero mesh with multiple boundaries e.g. face.m.
The output are the basis of holomorphic 1-forms,
- Holomorphic 1-form basis recorded as edge traits face_0.duv.m face_1.duv.m face_2.duv.m face_3.duv.m.
Convergence, Stability and Efficiency
The computational process is stable and converges fast.
Example
The input genus two mesh has 50k faces. The whole computational process takes about 30 seconds on a PC with 3.0 GB of RAM, 3.60 GHz CPU.
The data set and the source can be downloaded.
Command
- Compute the homology group basis:
slitmap.exe -cut face.m face
This generates face_0.cut.m face_1.cut.m face.cut.m
- Compute a fundamental domain:
slice face_0.cut.m face_0.open.m
- Slice the mesh along the cuts
slice face_1.cut.m face_1.open.m
slice face.cut.m face.open.m
- Compute the exact harmonic 1-forms:
slitmap -exact_form face.m face
This generates face_1.du.m face_2.du.m
- Compute the non-exact harmonic 1-forms:
slitmap -closed_form face.m face_0.open.m face_0.dv.m face_0.dv_uv.m
slitmap -closed_form face.m face_1.open.m face_1.dv.m face_1.dv_uv.m
The outputs are
face_0.dv.m face_0.dv_uv.m face_1.dv.m face_1.dv_uv.m
- Compute the holomorphic 1-form basis
slitmap.exe face_1.du.m face_2.du.m face_0.dv.m face_1.dv.m
This generates face_0.duv.m face_1.duv.m face_2.duv.m face_3.duv.m
- Integrate the holomorphic 1-forms on the fundamental domain
integrate.exe face_0.duv.m face.open.m face_0.uv.m
integrate.exe face_1.duv.m face.open.m face_1.uv.m
integrate.exe face_2.duv.m face.open.m face_2.uv.m
integrate.exe face_3.duv.m face.open.m face_3.uv.m
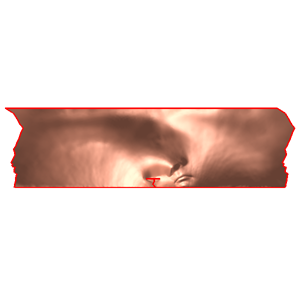
- Compute a special holomorphic 1-form, which maps the mesh to a stripe, two boundaries
are mapped to parallel lines, the other boundaries are mapped to horizontal slits
slitmap -slit_map face_0.duv.m face_1.duv.m face.duv.m
Integrate the holomorphic 1-form on the fundamental domain
integration face.duv.m face.open.m face.uv.m

|
|

|

|
|
face.uv.m
|
face.pos.m
|
face.uv1.m
|
face.pos1.m
|
















